Ocean freight, also known as sea freight, is the most common mode of transportation of goods internationally. Considered an integral part of global trade, ocean freight shipping is not just feasible for moving goods between countries but also a carbon-efficient option. And that’s possibly why approximately 90% of the world’s trade is conducted through this method.
But here’s what you must understand: the popularity of cargo shipping doesn’t mean that it’s the only transportation method of trade, or by any stretch, the best one From how soon you want the delivery to specific customs and regulatory requirements, you have to consider various aspects to decide which shipping method suits your business needs the most.
In this article, we’ll help you understand your options even within the spectrum of ocean freight. We will specifically explain full container load (FCL) and less than container load (LCL) — so that whichever mode of transportation you choose for your business is educated and sound. Let’s get started.
Understanding FCL and LCL
FCL and LCL are two distinct shipping methods — both offer different ways of control, transit times, and much more.
What Is FCL?

Full container load can be defined simply as a form of shipment in which the entire container is occupied; the space isn’t shared with other shippers so you are the one paying for the whole of the container.
Most shipping vessels provide different types of containers, varying in size as well as function. The common types of containers include refrigerated containers, dry containers, tank containers, platform containers, and collapsible containers.
FCL is ideal for large quantities of goods, substantial enough to cover a space roughly 20 to 40 feet tall.
Full container load is extremely convenient for shippers as you get complete control over the cargo.
Why Shippers Use FCL?
Some of the common reasons why shippers choose this shipping method are mentioned below:
- To make large shipments— it is ideal for manufacturers and wholesalers who want to transport bulks of goods.
- For the shipment of fragile goods— this mode is perfect for goods that require careful handling as rough handling can break or heighten the risk of damage.
- To get the best storage conditions— it ensures your goods are transported safely, following temperature-sensitivity guidelines, humidity levels, or any other storage conditions
- To ensure timely shipments— it’s best suited for time-sensitive shipments that require a predictable arrival time.
What is LCL?

Less than container load, on the other hand, is also called groupage and refers to containers filled with different orders. In this case, there are unique goods, each owned by different shippers.
The normal sizes for these containers vary from 8ft to 40ft. With LCL, you are essentially sharing space with other importers, making it a flexible and economical option for importers with a smaller stock. It is an ideal option for shipments between 1 to 10 CBM in weight.
How To Use LCL?
- Consolidate each shipment into a shared container
- Verify and document each shipment individually
- Transport the container to the port; for departure
- Once the container reaches its destination, each shipment is divided for delivery
Why do Shippers Use LCL?
- For smaller businesses— when the goods you’re shipping are less in quantity, not capable of filling an entire container
- Individuals shifting abroad — should you want to move your belongings to a location overseas
- Irregular shipments— it is an ideal case scenario for companies that are in their initial or testing phases and are simply unsure of the frequency at which their shipments will be moved
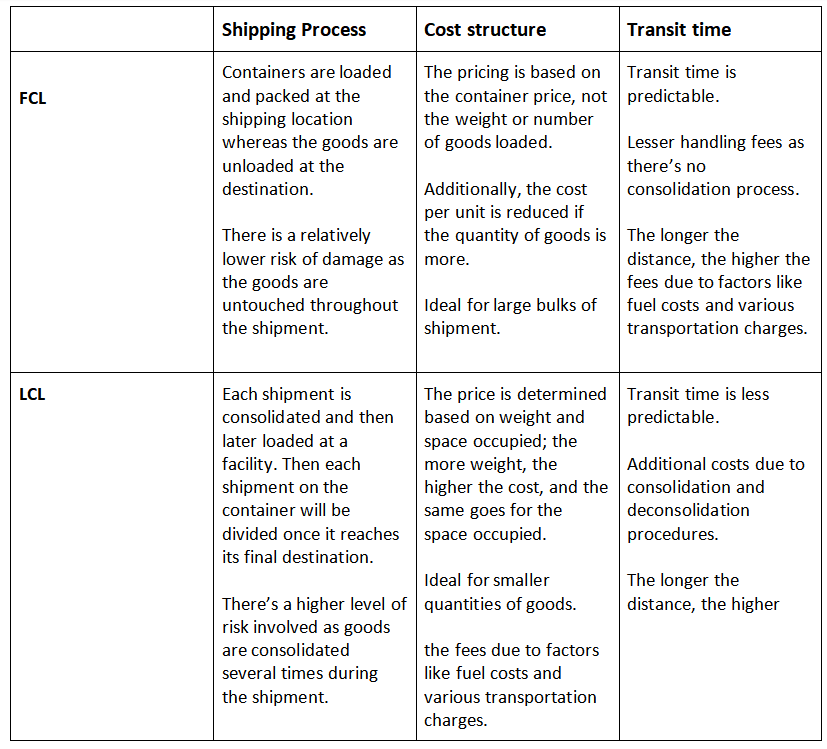
Key Differences Between FCL and LCL
Advantages of FCL
1. Control and Security
- Exclusive Use Of The Container: The entire container is dedicated to one shipper; this means fewer chances of mix-ups and enough space.
- Reduced Risk Of Damage Or Loss: Each item on the container is sealed at the time of its loading and unsealed only when the shipment reaches its destination. This maintains its integrity and minimizes damage.
2. Cost efficiency for larger shipments
- Economies of Scale:A highly feasible option for shipping a larger bulk of goods as the cost decreases with an increase in volume.
- Lower Cost Per Unit For High-Volume Shipments:The cost of shipment decreases with an increase in volume and bulk load which is in contrast with how things are done on an LCL.
3. Faster transit times
- Direct Shipping Routes:The routes are direct and predictable.
- Less Handling: The shipment is sealed at the port and opened only when it is delivered so there are fewer chances of mishandling.
Disadvantages of FCL
1. Higher cost for small shipments
- Inefficiency For Low-Volume Shipments: Not the most efficient method for fewer quantities of goods.
- Higher upfront costs: The cost for shipment and transportation fees is higher and more upfront.
2. Requirement for Large Volume
- Need For Sufficient Goods To Fill A Container:To get it rolling, you must ensure it is filled.
- Storage And Handling Challenges: Once it is sealed, you can’t undo it or make changes until it is unpacked in delivery.
Advantages of LCL
1. Cost efficiency for smaller shipments
- Pay Only For The Space Used: You only pay for the space your goods occupy, not the entire container
- No Need To Wait For Full Container Loads:You don’t have to fill the entire container with goods all by yourself, it’s a shared space.
2. Flexibility
- Suitable For Small To Medium-Sized Businesses: Ideal for smaller to medium businesses as they can easily transport their goods without having to buy an entire container.
- Easier to manage inventory and cash flow: The flexibility to ship fewer quantities of goods allows shippers to manage their inventories accurately and in a timely fashion.
3. Accessibility
- More frequent shipping schedules: LCLs are scheduled more frequently compared to FCL.
- Ideal For Trial Shipments Or Market Testing: This mode of transportation is less risky and cost-effective if you are new or testing a new shipment.
Disadvantages of LCL
1. Longer transit times
- Delays Due To Consolidation And Deconsolidation: The process of consolidating and deconsolidation can be time-consuming.
- Potential for multiple stops: Multiple stops along the way add unpredictability to transit time.
2. Increased risk of damage
- Mixed Cargo With Other Shippers’ Goods: It can easily be mixed with other shipments.
- More Handling During Transit: Due to multiple stops and shipments loaded, your goods will be handled quite a few times, increasing the risk of damage.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between FCL and LCL
Volume and weight of shipment
- Calculating total volume and weight: When choosing between FCL and LCL, keep the volume and weight of your shipment in check. If it’s enough to fill a container, FCL would be ideal for you, however, if you think otherwise, it’s best to share it with other shippers. LCL is best for first-time shippers.
- Comparing costs for FCL vs. LCL: LCL costs less compared to FCL if your goods don’t occupy the entire container; otherwise, the space goes wasted and the price becomes expensive. However, if you have a shipment that fills the container, FCL would be your best option as the cost decreases with the increase in volume.
Urgency of delivery
- Time sensitivity of the shipment:FCL has a more predictable time than LCL due to multiple pitstops. Therefore, keep the element of timing in mind before choosing the transportation method.
- Impact of transit times on business operations:If the deliveries are urgent, it’s best to consider your options. As mentioned, LCL is less predictable in transit.
Budget constraints
- Cost considerations and financial planning: Plan your budgets effectively. Ensure you are optimizing the cost-effective strategies. LCL is best for those with fewer goods whereas FCL is feasible for larger bulks.
- Balancing cost efficiency with shipping needs: Don’t neglect your shipping needs (fragile or temperature-sensitive goods) with the cost. Sometimes, it’s best to go for FCL even if the quantity of goods is less. It helps in shipping the goods in a more predictable and timely fashion.
Nature of goods
- Fragility and sensitivity of products:It’s best to weigh all your options for fragile and sensitive products. Do you want to risk the unpredictability and rough handling by choosing LCL or go with FCL where all the products are properly sealed and opened only at delivery?
- Special handling requirements: Make sure you choose the right option to avoid mishandling your goods; something that’s likely to happen should you choose LCL where multiple shipments are placed.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
Nike is a sportswear company that uses the FCL shipping method to transport shoes from its manufacturing factories in Asia to different retail shops and distribution centers globally. The same goes for IKEA, a world-class furniture retailer. They transport the flat-packed furniture from their manufacturing hubs to stores worldwide.
Samsung Electronics is yet another giant that depends heavily on FCL to ship its products worldwide from its main manufacturing market in Asia.
FCL is a dependable mode of transportation that allows companies to streamline their operations and establish a strong hold over their supply chains. Not only it help them minimize shipping costs but also regulates their inventories.
Small startups and e-commerce brands prefer using LCL as it helps them import goods cost-effectively. They can break into newer markets and continue the maintenance of minimal inventory. The upfront investment is also comparatively cheaper, reducing the budget strains on business owners.
Conclusion
To summarize, when choosing between Full Container Load (FCL) and Less than Container Load (LCL), put the cost, shipping procedures, and transit time of the shipment into consideration. There is no one-size-fits-all rule here that you can apply to navigate the challenges and benefits of Ocean freight shipment. Choose an option that suits your business needs.






